What is a Cloud Service Provider sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Imagine a world where data, applications, and computing power are accessible anytime, anywhere.
This is the reality of cloud computing, a paradigm shift that has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals interact with technology. At the heart of this revolution are Cloud Service Providers (CSPs), companies that offer a wide range of cloud-based services, enabling individuals and organizations to leverage the power of the cloud without the complexities of managing their own infrastructure.
From the humble beginnings of data storage and email services to the sophisticated platforms that power modern applications, CSPs have evolved to become essential components of the digital landscape. This exploration delves into the fascinating world of CSPs, unraveling the intricacies of their services, the benefits they offer, and the future trends shaping their evolution.
Introduction to Cloud Service Providers
The cloud computing landscape has undergone a remarkable transformation, revolutionizing how businesses and individuals access and utilize computing resources. Cloud computing is a paradigm shift that has moved away from traditional on-premises infrastructure towards a model where computing resources are delivered as a service over the internet.
Defining Cloud Service Providers
Cloud Service Providers (CSPs) are companies that deliver cloud computing services. These services encompass a wide range of offerings, including storage, compute power, databases, networking, and software. CSPs operate data centers and manage the underlying infrastructure, allowing users to access resources on demand, without the need for physical hardware or complex management tasks.
Prominent Cloud Service Providers
The cloud computing market is dominated by a few prominent CSPs, each with its unique strengths and offerings. These providers have established a significant presence in the industry and cater to a diverse range of customers.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS):A pioneer in cloud computing, AWS offers a comprehensive suite of services, including compute, storage, networking, databases, analytics, and artificial intelligence. Its global infrastructure and wide range of services make it a popular choice for businesses of all sizes.
- Microsoft Azure:Microsoft Azure provides a comprehensive cloud platform with a focus on hybrid cloud solutions. It offers a wide range of services, including compute, storage, databases, networking, and artificial intelligence. Azure’s integration with Microsoft products and its hybrid cloud capabilities make it attractive to organizations that are already using Microsoft technologies.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP):Google Cloud Platform leverages Google’s expertise in infrastructure, data analytics, and artificial intelligence. It offers a wide range of services, including compute, storage, databases, networking, and machine learning. GCP’s focus on innovation and its strong data analytics capabilities make it a popular choice for data-driven organizations.
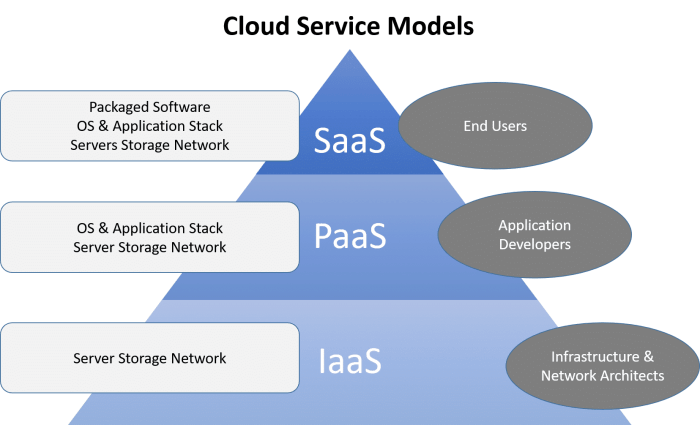
Types of Cloud Services

Cloud services offer a wide range of functionalities and cater to different needs and requirements. Understanding the different types of cloud services is crucial for choosing the right option for your specific needs.
Investigate the pros of accepting RMM for Internal IT in your business strategies.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides access to fundamental computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking. It allows users to manage and control their virtual infrastructure, giving them granular control over hardware resources.
- Virtual Machines (VMs):IaaS providers offer virtual machines, which are software-based representations of physical servers. Users can create, configure, and manage VMs according to their needs.
- Storage:IaaS platforms provide various storage options, including block storage, object storage, and file storage. Users can choose the storage type that best suits their data requirements.
- Networking:IaaS services offer virtual networks, allowing users to connect their VMs and other resources securely. They can configure firewalls, load balancers, and other network components.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides a platform for developing, running, and managing applications. It offers a complete development environment, including tools, libraries, and frameworks, simplifying the application development process.
- Development Environment:PaaS platforms provide pre-configured development environments with tools and libraries necessary for building applications. Developers can focus on coding without worrying about infrastructure setup.
- Runtime Environment:PaaS services manage the runtime environment for applications, ensuring they run smoothly and efficiently. They handle resource allocation, scaling, and security.
- Deployment and Management:PaaS platforms offer tools for deploying and managing applications. They provide features like automated deployment, monitoring, and logging.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS provides access to software applications over the internet. Users can access and use the software without installing or managing it on their own devices.
- Application Access:SaaS applications are accessed through a web browser or mobile app, making them readily available from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Centralized Management:SaaS providers manage the software infrastructure, updates, and security, freeing users from these responsibilities.
- Cost-Effectiveness:SaaS applications typically have a subscription-based pricing model, making them more affordable than traditional software licensing.
Comparison of Cloud Service Models
| Feature | IaaS | PaaS | SaaS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level of Abstraction | Low | Medium | High |
| Infrastructure Control | High | Limited | None |
| Application Development | User Responsibility | Platform Provided | Pre-built Applications |
| Examples | Amazon EC2, Google Compute Engine, Microsoft Azure | Heroku, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine | Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365, Google Workspace |
Benefits of Using Cloud Service Providers
Cloud service providers (CSPs) have revolutionized the way businesses and individuals access and utilize technology. By offering a wide range of services, including storage, computing power, and software applications, CSPs have enabled organizations of all sizes to streamline their operations, improve efficiency, and achieve their goals.
The benefits of using CSPs are numerous and can be categorized into several key areas.
Cost Savings
Adopting cloud services can significantly reduce operational costs for businesses. This is because CSPs handle the infrastructure, maintenance, and security, eliminating the need for businesses to invest in expensive hardware and IT personnel. The pay-as-you-go model offered by CSPs allows businesses to only pay for the resources they use, resulting in significant cost savings compared to traditional on-premises solutions.
For example, a small startup can leverage cloud computing to access powerful servers and software without the upfront investment required for physical infrastructure. This cost-effective approach enables startups to focus their resources on growth and innovation.
Scalability
Cloud services provide businesses with the ability to scale their resources up or down quickly and easily based on their changing needs. This is a significant advantage for businesses experiencing rapid growth or seasonal fluctuations in demand. With traditional on-premises infrastructure, scaling resources can be a time-consuming and costly process.
However, with cloud services, businesses can simply adjust their resource allocation with a few clicks, ensuring they have the necessary capacity to meet their needs. For instance, an e-commerce company can leverage cloud services to handle a surge in traffic during holiday sales without having to invest in additional hardware or software.
Flexibility
Cloud services offer businesses a high degree of flexibility, allowing them to access and utilize resources from anywhere in the world with an internet connection. This flexibility enables businesses to operate more efficiently and collaborate effectively, regardless of location. For example, a global company can utilize cloud-based collaboration tools to connect teams across different continents, fostering communication and productivity.
This flexibility also allows businesses to easily adopt new technologies and applications, accelerating their digital transformation journey.
Security
CSPs invest heavily in security infrastructure and expertise, offering businesses a higher level of security than they could typically achieve on their own. CSPs employ advanced security measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
They also adhere to industry-standard security certifications and compliance regulations, providing businesses with peace of mind knowing their data is safe and secure. For example, a financial institution can leverage cloud services to store and process sensitive customer data, knowing it is protected by robust security measures and compliance frameworks.
Key Features of Cloud Service Providers
Cloud service providers (CSPs) offer a diverse range of features and functionalities to cater to the needs of businesses and individuals alike. These features encompass various aspects, from data storage and computing power to network infrastructure and security measures, all designed to streamline operations and enhance efficiency.
Data Storage
CSPs provide secure and scalable data storage solutions, enabling users to store and manage their data efficiently. They offer various storage options, including object storage, block storage, and file storage, each tailored to specific use cases.
- Object storageis ideal for storing unstructured data, such as images, videos, and documents, offering high availability and durability.
- Block storageis suitable for storing structured data, such as databases and applications, providing low latency and high IOPS for performance-critical workloads.
- File storageis designed for sharing and accessing files, offering a familiar interface and compatibility with various operating systems.
Computing Power
CSPs offer a wide range of computing resources, including virtual machines (VMs), containers, and serverless computing, allowing users to scale their computing power on demand.
- Virtual machines (VMs)provide a virtualized environment for running operating systems and applications, offering flexibility and scalability.
- Containersare lightweight and portable packages that bundle applications and their dependencies, enabling rapid deployment and consistent execution across different environments.
- Serverless computingallows users to run code without managing servers, offering pay-as-you-go pricing and automatic scaling based on demand.
Network Infrastructure, What is a Cloud Service Provider
CSPs provide robust and reliable network infrastructure, enabling seamless connectivity and high-speed data transfer. They offer a range of network services, including content delivery networks (CDNs), virtual private networks (VPNs), and load balancers.
- Content delivery networks (CDNs)distribute content closer to users, reducing latency and improving website performance.
- Virtual private networks (VPNs)create secure connections over public networks, protecting sensitive data and enhancing privacy.
- Load balancersdistribute traffic across multiple servers, ensuring high availability and preventing server overload.
Security Measures
CSPs prioritize security, implementing robust measures to protect user data and applications. They offer a variety of security features, including encryption, access control, and threat detection.
- Encryptionsafeguards data in transit and at rest, preventing unauthorized access.
- Access controlrestricts access to resources based on user roles and permissions, ensuring data confidentiality.
- Threat detectionmonitors for malicious activities and vulnerabilities, providing proactive security measures.
Common Features of Cloud Service Providers
Most CSPs offer a set of common features, including:
- API access: Enables programmatic interaction with cloud services, facilitating automation and integration.
- Monitoring and logging: Provides insights into resource usage, performance, and security events.
- Support and documentation: Offers technical assistance and comprehensive documentation for cloud services.
- Scalability and elasticity: Allows users to adjust resources on demand, scaling up or down based on requirements.
- Pay-as-you-go pricing: Charges users only for the resources they consume, offering cost-effectiveness.
Choosing the Right Cloud Service Provider: What Is A Cloud Service Provider
Choosing the right cloud service provider (CSP) is crucial for businesses of all sizes, as it can significantly impact their success. The decision should not be taken lightly, as it involves factors that can influence cost, performance, security, and overall business strategy.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a CSP
Selecting the right CSP requires careful consideration of various factors that align with specific business needs. These factors can be categorized into several key areas:
- Service Offerings:The CSP should offer the services your business requires, including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Determine the specific services you need, such as virtual machines, databases, storage, networking, and application development tools.
- Scalability and Flexibility:The CSP should be able to scale its resources up or down as your business needs change. This is essential for businesses that experience fluctuating workloads or seasonal peaks.
- Security and Compliance:Data security is paramount. Ensure the CSP offers robust security measures, including data encryption, access control, and compliance with relevant industry standards and regulations.
- Pricing and Cost Management:Different CSPs have varying pricing models. Consider factors like pay-as-you-go, reserved instances, and discounts. Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including setup fees, ongoing costs, and potential support expenses.
- Reliability and Availability:Choose a CSP with a proven track record of high uptime and availability. Consider their service level agreements (SLAs) and disaster recovery capabilities.
- Customer Support and Documentation:Ensure the CSP offers adequate customer support, including 24/7 availability and comprehensive documentation. This is crucial for resolving issues and getting the most out of the services.
- Industry Focus and Expertise:Some CSPs specialize in specific industries, such as healthcare, finance, or retail. Consider choosing a CSP with expertise in your industry to ensure they understand your specific needs and challenges.
- Integration and Compatibility:The CSP should integrate well with your existing IT infrastructure and applications. Check for compatibility with your preferred operating systems, programming languages, and tools.
- Location and Data Sovereignty:Consider the location of the CSP’s data centers and ensure compliance with data sovereignty regulations. This is particularly important for businesses handling sensitive data.
Comparing Different CSPs
Once you have identified your specific needs and requirements, it’s time to compare different CSPs based on their offerings and capabilities. Here’s a breakdown of key areas to focus on:
- Pricing Models:CSPs typically offer different pricing models, including pay-as-you-go, reserved instances, and discounts. Compare pricing structures, calculate the total cost of ownership, and consider the long-term financial implications of each model.
- Service Levels:Evaluate the service level agreements (SLAs) offered by different CSPs. This includes uptime guarantees, response times, and support availability. Choose a CSP with SLAs that meet your business requirements.
- Industry Focus:Consider CSPs with expertise in your specific industry. This ensures they understand your unique needs, regulations, and best practices. Look for CSPs that offer industry-specific solutions and support.
Evaluating and Choosing the Most Suitable CSP
Choosing the right CSP is a multi-step process that involves careful evaluation and comparison. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Define Your Needs and Requirements:Clearly identify your business needs, including the types of cloud services you require, the required scalability, security standards, and budget constraints.
- Research and Shortlist CSPs:Research different CSPs, including major players like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP), as well as niche providers specializing in specific industries or services. Shortlist a few CSPs that appear to meet your requirements.
- Request Proposals (RFPs):Send RFPs to your shortlisted CSPs, outlining your specific needs, technical requirements, and budget. This allows for a standardized comparison of proposals.
- Evaluate Proposals and Conduct Due Diligence:Carefully evaluate the proposals, focusing on pricing, service levels, security measures, and industry expertise. Conduct due diligence, including customer references and independent reviews, to assess the CSP’s reputation and reliability.
- Pilot Projects and Proof of Concepts (POCs):Consider conducting pilot projects or POCs with your preferred CSPs to test their services and validate their performance. This helps to ensure a smooth transition and minimize risks.
- Negotiate Contracts and Agreements:Negotiate favorable terms and conditions, including pricing, SLAs, and security provisions. Ensure the contract clearly Artikels the responsibilities of both parties.
- Implement and Monitor:Once you have chosen a CSP, implement the chosen services and monitor their performance closely. Regularly review your cloud strategy and make adjustments as needed to optimize your cloud environment.
Future Trends in Cloud Computing
The cloud computing landscape is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changing user demands. This dynamic environment is shaping the future of cloud services and their impact on the digital landscape.
Edge Computing
Edge computing is gaining significant traction as a way to reduce latency and improve performance by bringing computation and data storage closer to users. It involves processing data at the edge of the network, closer to the source of the data, rather than relying solely on centralized cloud data centers.
- Reduced Latency:Edge computing minimizes the distance data travels, resulting in faster response times and improved user experiences, particularly for applications requiring real-time data processing, such as streaming, gaming, and IoT devices.
- Enhanced Security:Processing data closer to the source can enhance security by reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access, especially in environments with sensitive data.
- Increased Bandwidth Efficiency:By processing data locally, edge computing can reduce the amount of data transmitted to the cloud, leading to more efficient use of bandwidth and network resources.
Serverless Computing
Serverless computing is an emerging paradigm that allows developers to run code without managing servers. CSPs handle the underlying infrastructure, including provisioning, scaling, and maintenance, allowing developers to focus on writing code and delivering applications.
- Cost Efficiency:Developers only pay for the resources they use, reducing infrastructure costs and improving cost optimization.
- Scalability and Elasticity:Serverless computing automatically scales resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency.
- Faster Development Cycles:Developers can deploy and iterate code quickly without worrying about server management, leading to faster development cycles and quicker time to market.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is revolutionizing cloud computing, enabling CSPs to offer intelligent services that enhance efficiency, security, and user experience.
- Automated Operations:AI-powered tools automate routine tasks, such as infrastructure management, security monitoring, and performance optimization, freeing up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Enhanced Security:AI algorithms can detect and respond to threats in real-time, improving security posture and reducing the risk of data breaches.
- Personalized Experiences:AI enables CSPs to deliver personalized services based on user preferences and behavior, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Outcome Summary
As we navigate the ever-evolving digital landscape, the role of Cloud Service Providers continues to expand, offering businesses and individuals unprecedented opportunities to innovate, grow, and thrive. By understanding the fundamentals of CSPs, their diverse service offerings, and the factors that drive their evolution, we gain valuable insights into the future of technology and its impact on our lives.
The journey into the world of CSPs is a captivating one, filled with possibilities and innovations that promise to shape the future of our digital world.
Popular Questions
What are some of the most popular Cloud Service Providers?
Some of the most prominent CSPs in the market include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), IBM Cloud, and Alibaba Cloud. These companies offer a wide range of cloud services and cater to diverse business needs.
How do I choose the right Cloud Service Provider for my needs?
Selecting the right CSP involves considering factors such as your budget, the specific services you require, your data security needs, and the level of support you need. It’s essential to evaluate the pricing models, service levels, and industry focus of different CSPs before making a decision.
What are the security implications of using Cloud Service Providers?
While CSPs offer robust security measures, it’s crucial to understand the security protocols they implement and ensure that your data is adequately protected. You should also be aware of potential risks and vulnerabilities associated with cloud services and take appropriate steps to mitigate them.
What are the future trends in Cloud Computing?
The future of cloud computing is exciting, with emerging trends like edge computing, serverless computing, and AI poised to revolutionize the way we interact with the cloud. These technologies will enable faster processing, enhanced scalability, and more personalized experiences, further shaping the digital landscape.