Comparing AWS and Azure Storage Pricing and Features is a crucial step for any business looking to leverage the power of cloud storage. Both AWS and Azure offer a comprehensive suite of storage services, each with its own unique pricing models and feature sets.
Understanding these differences is essential for making informed decisions about which platform best suits your specific needs and budget.
This guide dives deep into the intricacies of AWS and Azure storage, comparing their pricing structures, key features, and suitability for various use cases. We’ll explore the advantages and disadvantages of each platform’s offerings, providing real-world examples and actionable insights to help you navigate the complex world of cloud storage.
Cloud Storage: AWS vs. Azure
A Deep Dive into Pricing and Features
Cloud storage has become a vital component of modern businesses, offering a scalable, reliable, and cost-effective way to store and manage data. As cloud computing giants, Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure dominate the cloud storage market, each offering a comprehensive suite of services to meet diverse storage needs.
Choosing the right cloud storage provider can significantly impact your business’s bottom line and operational efficiency. This in-depth analysis delves into the intricacies of AWS and Azure storage pricing and features, providing you with the necessary insights to make an informed decision.
AWS Storage Offerings
AWS provides a wide range of storage services, each designed for specific use cases and data types. Understanding the nuances of each service is crucial for optimizing your storage strategy and maximizing cost efficiency.
- Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service):The foundation of AWS storage, S3 offers a highly scalable and durable object storage service. It’s ideal for storing data like backups, website content, and multimedia files. S3 provides multiple storage classes, each with different price points and performance characteristics, allowing you to tailor your storage strategy to your specific requirements.
- Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Storage):Designed for persistent block storage for EC2 instances, EBS provides high-performance, low-latency storage for applications that require fast data access. EBS offers various volume types, each with different performance and pricing, allowing you to choose the best fit for your workload.
- Amazon Glacier:A cost-effective, highly durable, and secure storage service designed for long-term data archiving. Glacier is ideal for storing data that is rarely accessed, such as backups, legal documents, and historical data.
- Amazon EFS (Elastic File System):A fully managed file system that provides a scalable, high-performance, and POSIX-compliant file system for use with EC2 instances. EFS is ideal for applications that require shared access to files, such as web servers, databases, and application servers.
AWS Storage Services: Comparing AWS And Azure Storage Pricing And Features
AWS offers a wide range of storage services designed to meet diverse needs, from storing static websites to managing databases and running high-performance applications. Understanding the differences between these services is crucial for selecting the most appropriate option for your specific use case.
AWS Storage Services Comparison
The table below compares key AWS storage services, outlining their characteristics, pricing models, and typical use cases. | Service Name | Description | Pricing Model | Key Features | Use Cases ||—|—|—|—|—|| Amazon S3 | Object storage for data of all types | Per GB per month | High availability, scalability, and durability | Website hosting, data backups, media streaming, and data archiving || Amazon EBS | Block storage for EC2 instances | Per GB per month | High performance, low latency, and persistent storage | Databases, application servers, and other performance-critical workloads || Amazon EFS | File storage for EC2 instances | Per GB per month | Scalable, shared file system accessible by multiple EC2 instances | Shared file systems for web servers, databases, and other applications || Amazon Glacier | Archival storage for long-term data retention | Per GB per month | Low-cost storage for data rarely accessed | Data backups, compliance archiving, and long-term data retention || Amazon S3 Glacier Deep Archive | Archival storage for data with extremely low access frequency | Per GB per month | Extremely low-cost storage for data accessed infrequently | Long-term data retention, data backups, and compliance archiving |
Advantages and Disadvantages of AWS Storage Services
Each AWS storage service has its own advantages and disadvantages, making it essential to carefully consider your specific needs before choosing a service.
Amazon S3
Advantages:
High Availability and Durability
Amazon S3 is designed for high availability and durability, with data replicated across multiple availability zones.
Scalability
Amazon S3 can easily scale to handle large amounts of data, making it ideal for growing businesses.
Cost-Effective
Amazon S3 offers a cost-effective solution for storing data, especially for large volumes.
Wide Range of Features
Amazon S3 provides a wide range of features, including versioning, lifecycle management, and encryption. Disadvantages:
Not Suitable for Frequent Access
Amazon S3 is not designed for frequent access and can incur high latency for frequent read/write operations.
Limited Functionality
While Amazon S3 offers a wide range of features, it lacks some advanced features available in other storage services.
Amazon EBS
Advantages:
High Performance
Amazon EBS provides high performance and low latency, making it ideal for performance-critical workloads.
Persistent Storage
Amazon EBS provides persistent storage, meaning data is preserved even when an EC2 instance is stopped or terminated.
Integration with EC2
Amazon EBS is tightly integrated with Amazon EC2, making it easy to attach and detach volumes. Disadvantages:
Costly
Amazon EBS is more expensive than Amazon S3, especially for large volumes of data.
Limited Scalability
Amazon EBS volumes have a limited size, which can be a constraint for large workloads.
Amazon EFS
Advantages:
Scalability
Amazon EFS can easily scale to handle large amounts of data and users.
Shared File System
Amazon EFS provides a shared file system that can be accessed by multiple EC2 instances.
Integration with EC2
Amazon EFS is tightly integrated with Amazon EC2, making it easy to mount and unmount file systems. Disadvantages:
Higher Latency
Amazon EFS can have higher latency compared to Amazon EBS, especially for frequent read/write operations.
Limited Functionality
Amazon EFS lacks some advanced features available in other storage services, such as object versioning.
Amazon Glacier
Advantages:
Low Cost
Amazon Glacier offers extremely low-cost storage for data that is rarely accessed.
High Durability
Amazon Glacier is designed for high durability, with data replicated across multiple availability zones.
Data Retention
Amazon Glacier is ideal for long-term data retention, such as backups and compliance archiving. Disadvantages:
High Latency
Amazon Glacier has high latency for data retrieval, making it unsuitable for frequently accessed data.
Limited Functionality
Amazon Glacier lacks some advanced features available in other storage services, such as object versioning.
Amazon S3 Glacier Deep Archive
Advantages:
Extremely Low Cost
Amazon S3 Glacier Deep Archive offers the lowest cost storage for data accessed infrequently.
High Durability
Amazon S3 Glacier Deep Archive is designed for high durability, with data replicated across multiple availability zones.
Data Retention
Amazon S3 Glacier Deep Archive is ideal for long-term data retention, such as backups and compliance archiving. Disadvantages:
Very High Latency
Amazon S3 Glacier Deep Archive has very high latency for data retrieval, making it unsuitable for frequently accessed data.
Limited Functionality
Amazon S3 Glacier Deep Archive lacks some advanced features available in other storage services, such as object versioning.
Real-World Examples of AWS Storage Services
AWS storage services are widely used in real-world scenarios, demonstrating their versatility and adaptability. * Website Hosting:Amazon S3 is commonly used for hosting static websites, leveraging its high availability, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
Data Backups
Amazon Glacier and Amazon S3 Glacier Deep Archive are frequently used for long-term data backups, providing a cost-effective solution for storing data rarely accessed.
Media Streaming
Amazon S3 is used for storing and streaming media content, enabling businesses to deliver high-quality video and audio experiences.
Database Storage
Amazon EBS is used for storing databases, providing high performance and persistent storage for critical workloads.
Shared File Systems
Amazon EFS is used for creating shared file systems, enabling multiple EC2 instances to access and collaborate on data.
Azure Storage Services
Azure storage services are a critical component of Microsoft’s cloud platform, offering a diverse range of options for storing and managing data. These services are designed to handle various data types and workloads, from simple object storage to high-performance disk storage.
Azure Storage Services Comparison
Azure storage services cater to different storage needs and use cases. The following table compares key features and characteristics of popular Azure storage services:| Service Name | Description | Pricing Model | Key Features | Use Cases ||—|—|—|—|—|| Blob Storage| Stores unstructured data like images, videos, documents, and backups.
| Pay-as-you-go based on storage capacity and data transfer. | High availability, scalability, and durability. Supports various access tiers for cost optimization. | Storing website content, media files, backups, and archival data. || File Storage| Provides SMB file shares accessible via the network.
| Pay-as-you-go based on storage capacity and data transfer. | Offers file sharing capabilities similar to traditional file servers. Integrates with Windows and Linux environments. | Sharing files among users and applications, providing file server functionality in the cloud.
|| Disk Storage| Provides persistent block storage for virtual machines (VMs) and other cloud services. | Pay-as-you-go based on storage capacity and IOPS. | Offers high performance and low latency for applications demanding high I/O throughput. | Providing storage for VMs, databases, and other performance-critical applications.
|| Queue Storage| Stores messages for asynchronous communication between applications. | Pay-as-you-go based on message storage and transactions. | Supports message queuing for decoupling applications and handling high-volume message processing. | Implementing message queues for asynchronous tasks, event processing, and decoupling applications.
|| Table Storage| Stores structured NoSQL data in tables with rows and columns. | Pay-as-you-go based on storage capacity and transactions. | Provides a flexible and scalable database solution for unstructured data. | Storing user profiles, sensor data, and other semi-structured data.
|
Advantages and Disadvantages of Azure Storage Services
Each Azure storage service has unique advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for specific scenarios: Blob Storage:
Advantages
Highly scalable, cost-effective, and suitable for storing large amounts of unstructured data.
Disadvantages
Limited querying capabilities compared to other databases. File Storage:
Advantages
Provides familiar file sharing capabilities, seamlessly integrates with existing file systems.
Disadvantages
Less scalable and flexible than Blob Storage for unstructured data. Disk Storage:
Advantages
Offers high performance and low latency, ideal for demanding applications.
Disadvantages
More expensive than other storage options due to its performance characteristics. Queue Storage:
Advantages
Provides reliable and scalable message queuing, enabling asynchronous communication.
Disadvantages
Limited data storage capabilities, primarily used for message handling. Table Storage:
Advantages
Provides a scalable and flexible NoSQL database solution for semi-structured data.
Disadvantages
Less structured than traditional relational databases, may require more complex data modeling.
Real-World Use Cases of Azure Storage Services
Azure storage services are widely used in various real-world scenarios:* Blob Storage:Storing website content for a global e-commerce platform, archiving customer data for compliance purposes, and backing up critical business applications.
File Storage
Providing file sharing for a collaborative team working on a large project, hosting a shared file server for a small business.
Disk Storage
Providing persistent storage for a high-performance database server, running a virtual machine with demanding I/O requirements.
Queue Storage
Processing large volumes of user requests in an e-commerce website, handling asynchronous events in a financial trading platform.
Table Storage
Storing user profiles and preferences in a social media application, collecting and analyzing sensor data from IoT devices.
Comparison of Pricing Models
Understanding the pricing models of AWS and Azure storage services is crucial for optimizing costs and making informed decisions about which platform best suits your specific needs. Both providers offer a diverse range of storage options, each with its unique pricing structure.
Storage Capacity Pricing
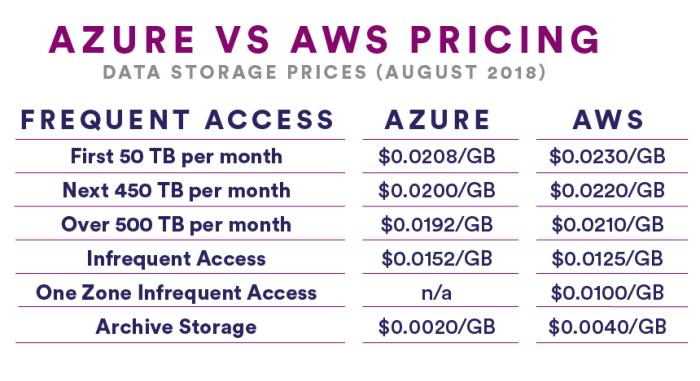
The cost of storage capacity is a fundamental factor in determining the overall cost of cloud storage. Both AWS and Azure charge for storage based on the amount of data stored.
- AWS S3:Charges per GB per month for storage, with discounts available for storing data for longer periods.
- Azure Blob Storage:Charges per GB per month for storage, with discounts available for storing data for longer periods.
The pricing for storage capacity can vary significantly depending on the storage class chosen. For example, AWS S3 offers different storage classes, such as Standard, Infrequent Access (IA), Glacier, and Glacier Deep Archive, each with varying pricing based on access frequency and data retention requirements.
Similarly, Azure Blob Storage offers different tiers, including Hot, Cool, and Archive, each with varying pricing based on access frequency and data retention requirements.
Data Transfer Pricing
Data transfer charges encompass the costs associated with moving data into, out of, and within the cloud storage service. Both AWS and Azure charge for data transfer based on the volume of data transferred and the distance it travels.
- AWS:Charges for data transfer based on the source and destination of the data. For example, transferring data from an EC2 instance to S3 is typically less expensive than transferring data from an on-premises server to S3.
- Azure:Charges for data transfer based on the source and destination of the data. Similar to AWS, transferring data within Azure is typically less expensive than transferring data from an on-premises server to Azure.
API Request Pricing
API requests are essential for interacting with cloud storage services, and both AWS and Azure charge for these requests. The pricing for API requests typically varies based on the type of request, such as GET, PUT, or DELETE, and the specific storage service used.
- AWS:Charges for API requests based on the type of request and the storage service used. For example, requests to S3 are priced differently than requests to EBS.
- Azure:Charges for API requests based on the type of request and the storage service used. For example, requests to Blob Storage are priced differently than requests to File Storage.
Cost Implications for Different Use Cases
The cost implications of using different storage services vary depending on the specific use case. For example, if a business requires frequent access to large amounts of data, it may be more cost-effective to use a storage service with lower storage capacity pricing but higher data transfer costs.
Conversely, if a business stores large amounts of infrequently accessed data, it may be more cost-effective to use a storage service with higher storage capacity pricing but lower data transfer costs.
Scenario: AWS vs. Azure
Consider a scenario where a business needs to store large amounts of video content for on-demand streaming. The business expects high data transfer volumes due to user requests.
- AWS:If the business prioritizes cost optimization for data transfer, AWS S3 with its tiered pricing for data transfer might be more advantageous. The business can leverage lower data transfer costs for frequently accessed content, potentially offsetting higher storage costs for less frequently accessed content.
- Azure:If the business prioritizes cost optimization for storage capacity, Azure Blob Storage with its tiered pricing for storage might be more advantageous. The business can leverage lower storage costs for large volumes of video content, potentially offsetting higher data transfer costs.
Comparison of Key Features
When choosing between AWS and Azure storage services, it’s crucial to consider the key features that align with your specific needs. Both platforms offer a robust set of features, but they differ in their strengths and weaknesses.
Data Security
Data security is paramount in cloud storage. Both AWS and Azure provide comprehensive security features to protect your data.
- AWSoffers features like encryption at rest, encryption in transit, access control lists (ACLs), and multi-factor authentication (MFA). AWS also provides robust security auditing and compliance certifications, such as SOC 2, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
- Azurealso offers encryption at rest and in transit, along with role-based access control (RBAC), MFA, and Azure Active Directory integration. Azure also boasts compliance certifications like ISO 27001, HIPAA, and GDPR.
Scalability
Scalability is essential for handling fluctuating storage demands. Both platforms excel in this area.
- AWSprovides a highly scalable infrastructure, allowing you to seamlessly adjust storage capacity based on your needs. AWS’s services like S3 and EBS offer near-infinite scalability, making them suitable for applications with unpredictable storage requirements.
- Azurealso offers excellent scalability, allowing you to easily scale storage resources up or down. Azure’s Blob storage and Disk storage services provide on-demand scalability, ensuring you have the right amount of storage at any given time.
Availability
High availability is crucial for ensuring uninterrupted access to your data. Both platforms offer high availability through redundant infrastructure and data replication.
- AWSboasts a global network of data centers with multiple availability zones in each region. This ensures data redundancy and fault tolerance, minimizing downtime in the event of a failure.
- Azurealso employs a geographically distributed network of data centers with multiple availability zones. Azure’s services like Blob storage and Disk storage offer high availability through automatic replication and failover mechanisms.
Performance
Performance is critical for applications that require fast data access and processing. Both platforms provide high-performance storage services, but their performance characteristics may vary depending on the specific service and use case.
- AWSoffers a wide range of storage services optimized for different performance needs. For example, AWS S3 Standard-IA is designed for low-frequency access, while AWS S3 Standard is optimized for high-frequency access.
- Azurealso provides various storage services with different performance characteristics. Azure Blob storage offers different tiers based on performance requirements, such as Hot, Cool, and Archive tiers.
Comparison Table
| Feature | AWS | Azure ||—|—|—|| Data Security | Encryption at rest, encryption in transit, ACLs, MFA, security auditing, compliance certifications | Encryption at rest, encryption in transit, RBAC, MFA, Azure Active Directory integration, compliance certifications || Scalability | Highly scalable infrastructure, near-infinite scalability for services like S3 and EBS | Excellent scalability, on-demand scalability for Blob storage and Disk storage || Availability | High availability through global network of data centers with multiple availability zones | High availability through geographically distributed network of data centers with multiple availability zones || Performance | Wide range of storage services optimized for different performance needs | Various storage services with different performance characteristics, including tiers based on performance requirements |
Use Case Analysis
Cloud storage services are widely used across various industries and applications. Understanding the specific needs of different use cases can help you choose the most suitable storage service from AWS or Azure. This section analyzes common use cases and compares the suitability of AWS and Azure storage services for each.
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
Data backup and disaster recovery are crucial for any organization, ensuring data protection and business continuity. AWS and Azure offer a range of storage services for these purposes, each with its strengths and weaknesses.
- AWS S3:AWS Simple Storage Service (S3) is a highly scalable and durable object storage service that can be used for backing up data and creating disaster recovery solutions. S3 offers various storage classes, including Standard, Standard-IA, and Glacier, allowing you to optimize storage costs based on data access frequency.AWS S3 also supports versioning, enabling you to restore data to previous versions in case of accidental deletion or corruption.
- Azure Blob Storage:Azure Blob Storage is a similar object storage service to AWS S3, providing high availability, scalability, and durability for data backup and disaster recovery. Azure Blob Storage offers different storage tiers, including Hot, Cool, and Archive, to manage storage costs based on access patterns.Azure Blob Storage also supports versioning, ensuring data recovery in case of errors.
For data backup and disaster recovery, both AWS S3 and Azure Blob Storage are suitable options. The choice depends on factors like cost optimization, access frequency, and specific features offered by each service.
Web Hosting and Content Delivery
Cloud storage services are essential for web hosting and content delivery, enabling fast and reliable access to website files and multimedia content. AWS and Azure offer various services for web hosting and content delivery.
- AWS S3:AWS S3 can be used for static website hosting, delivering website files directly from S3 buckets. AWS also offers CloudFront, a global content delivery network (CDN), to cache website content at edge locations, reducing latency and improving performance for users worldwide.
- Azure Blob Storage:Azure Blob Storage can also be used for static website hosting. Azure CDN is a similar service to CloudFront, offering content caching and delivery at edge locations, enhancing website performance.
AWS S3 and Azure Blob Storage are both viable options for web hosting and content delivery, providing scalable and reliable storage for website files and multimedia content. The choice depends on specific needs, such as integration with other services, pricing models, and available features.
Big Data Analytics
Big data analytics involves processing and analyzing large datasets to extract valuable insights. Cloud storage services are crucial for storing and accessing big data, enabling efficient analysis and processing.
- AWS S3:AWS S3 is a popular choice for storing big data, offering high scalability and durability. S3 integrates seamlessly with other AWS services, such as Amazon EMR (Elastic MapReduce) and Amazon Athena, enabling data analysis and processing using various tools and frameworks.
- Azure Blob Storage:Azure Blob Storage is another suitable option for storing big data, providing scalability and cost-effectiveness. Azure Blob Storage integrates with Azure Data Lake Storage, enabling data analysis and processing using tools like Azure Databricks and Azure Synapse Analytics.
For big data analytics, both AWS S3 and Azure Blob Storage are suitable options, offering storage and integration with various data processing tools and frameworks. The choice depends on specific needs, such as integration with other services, pricing models, and data processing requirements.
Media and Entertainment, Comparing AWS and Azure Storage Pricing and Features
The media and entertainment industry relies heavily on cloud storage services for storing and distributing large media files, such as videos, audio, and images. AWS and Azure offer specialized services for media storage and delivery.
- AWS S3:AWS S3 is commonly used for storing media files, offering high scalability and durability. AWS also offers MediaStore, a service specifically designed for storing and delivering media content, providing low latency and high throughput.
- Azure Blob Storage:Azure Blob Storage is also suitable for storing media files, offering scalability and cost-effectiveness. Azure Media Services provides a comprehensive solution for managing and delivering media content, including encoding, transcoding, and content protection.
For media and entertainment, AWS S3 and Azure Blob Storage are both suitable options, providing storage and specialized services for managing and delivering media content. The choice depends on specific needs, such as content protection, encoding requirements, and integration with other services.
Healthcare
The healthcare industry requires secure and compliant storage solutions for sensitive patient data, such as medical records and images. AWS and Azure offer services that meet the specific requirements of the healthcare industry.
- AWS S3:AWS S3 offers compliance with HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), ensuring the security and privacy of patient data. AWS also provides services like Amazon Comprehend Medical for analyzing medical text and extracting insights from patient records.
- Azure Blob Storage:Azure Blob Storage also meets HIPAA compliance, providing secure and compliant storage for patient data. Azure also offers services like Azure Cognitive Services for healthcare, enabling analysis and insights from medical data.
For healthcare, AWS S3 and Azure Blob Storage are both suitable options, providing secure and compliant storage for patient data. The choice depends on specific needs, such as integration with other services, data analytics capabilities, and compliance requirements.
Conclusion
The choice between AWS and Azure storage depends on your specific needs and requirements. Both platforms offer a wide range of storage services with varying features and pricing models. This in-depth comparison provides a comprehensive overview of their offerings, helping you make an informed decision.
Key Findings
The comparison revealed that AWS and Azure offer a comparable range of storage services. Both platforms cater to different needs, from basic object storage to specialized solutions like data lakes and archival storage. AWS stands out with its vast global infrastructure, offering a wider selection of regions and availability zones.
Azure excels in its integration with other Microsoft products and services, providing a seamless experience for businesses using the Microsoft ecosystem.
Choosing the Right Platform
To choose the best platform, consider the following factors:
- Pricing Model:AWS and Azure offer different pricing models for their storage services. AWS often charges based on data storage and retrieval, while Azure uses a tiered pricing model with different pricing tiers based on storage frequency and access patterns. Carefully analyze your storage needs and usage patterns to determine the most cost-effective option.
- Features:Evaluate the specific features offered by each platform, such as data replication, security, and compliance. If you require specific features like cold storage, data analytics, or high-performance storage, ensure the chosen platform supports them.
- Integration with Existing Systems:Consider the ease of integration with your existing infrastructure and applications. Azure offers better integration with Microsoft products and services, while AWS provides more flexibility and integration with third-party tools.
- Scalability and Performance:Determine your storage needs in terms of scalability and performance. Both platforms offer scalable solutions, but AWS typically provides a larger global footprint and potentially faster performance for certain use cases.
Recommendations
- For businesses heavily invested in the Microsoft ecosystem, Azure offers a seamless integration experience and might be a more suitable option.
- For businesses requiring a global footprint and a wider range of availability zones, AWS could be a better choice.
- For cost-sensitive applications, carefully analyze the pricing models of both platforms and select the one that aligns best with your storage needs and usage patterns.
Ultimately, the best cloud storage platform depends on your unique requirements. A thorough analysis of your specific needs, including cost, features, scalability, and integration, will help you make the right decision for your business.
Wrap-Up
Ultimately, the choice between AWS and Azure storage boils down to your specific requirements and priorities. If cost-effectiveness is paramount, Azure might be the better option. However, if you value robust security features and a wide range of services, AWS could be the ideal choice.
By carefully considering your use cases, budget, and long-term goals, you can make an informed decision that optimizes your cloud storage strategy and unlocks the full potential of your data.
Expert Answers
What are the main differences between AWS and Azure storage?
AWS and Azure offer a wide range of storage services, but they differ in pricing models, features, and specific use cases. For example, AWS S3 is known for its low cost and scalability, while Azure Blob Storage excels in data transfer speeds.
Understanding these nuances is crucial for selecting the right platform.
How can I choose the best storage service for my WordPress website?
For WordPress websites, consider factors like website traffic, storage needs, and budget. If you need high-performance storage for dynamic content, AWS EBS might be suitable. For static content and backups, Azure Blob Storage offers cost-effective options.
Are there any security considerations when choosing between AWS and Azure?
Both AWS and Azure offer robust security features, including encryption, access control, and compliance certifications. However, it’s important to research the specific security protocols and certifications offered by each platform to ensure they meet your requirements.