HRIS Systems for Small Companies are revolutionizing the way businesses manage their human resources. By automating tasks, simplifying processes, and providing valuable insights, HRIS systems offer a plethora of benefits for companies of all sizes, particularly for smaller organizations that may not have dedicated HR departments.
From employee onboarding and payroll management to performance tracking and talent development, HRIS systems can streamline HR operations, freeing up time for HR professionals to focus on strategic initiatives and employee engagement. These systems provide a centralized platform for managing employee data, ensuring compliance with regulations, and enhancing overall efficiency.
Introduction to HRIS Systems
An HRIS (Human Resources Information System) is a software solution designed to manage and streamline various HR functions within an organization. It consolidates and centralizes employee data, automating tasks and providing valuable insights for informed decision-making.HRIS systems have become increasingly popular, particularly for small companies seeking to improve efficiency and reduce administrative burdens.
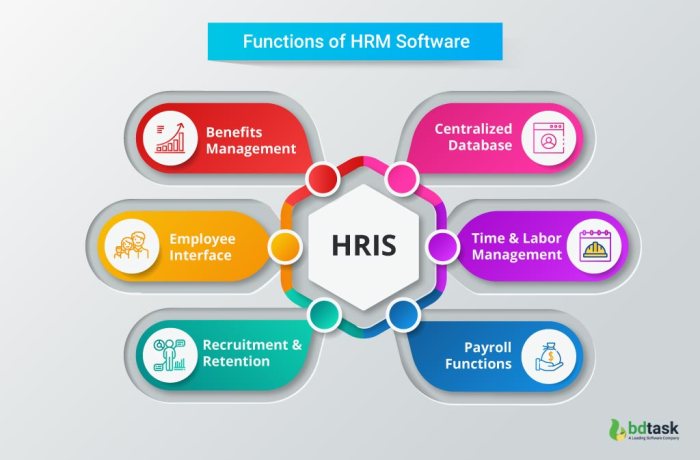
Core Functionalities of an HRIS System
HRIS systems offer a comprehensive suite of functionalities to manage various aspects of the employee lifecycle. These include:
- Employee Data Management:HRIS systems act as a central repository for employee information, such as contact details, employment history, payroll data, benefits, and performance records. This ensures data accuracy and accessibility for authorized personnel.
- Recruitment and Onboarding:HRIS systems streamline the recruitment process by providing tools for job posting, applicant tracking, and onboarding new hires. They facilitate efficient communication, automate tasks, and provide a standardized onboarding experience.
- Payroll and Compensation:HRIS systems integrate with payroll systems to automate payroll processing, deductions, and tax calculations. They also help manage benefits administration, including health insurance, retirement plans, and time off.
- Performance Management:HRIS systems provide tools for performance reviews, goal setting, and employee development. They facilitate regular feedback, track progress, and identify areas for improvement.
- Training and Development:HRIS systems can manage training programs, track employee certifications, and facilitate online learning. They provide a platform for delivering training materials and assessing employee progress.
- Reporting and Analytics:HRIS systems generate reports and dashboards that provide insights into workforce demographics, employee engagement, turnover rates, and other key HR metrics. These insights help organizations make informed decisions and optimize HR strategies.
Benefits of Using an HRIS for Small Companies
Adopting an HRIS can significantly benefit small companies by:
- Increased Efficiency:Automating HR processes frees up time for HR professionals to focus on strategic initiatives. It reduces manual tasks, minimizes errors, and streamlines workflows.
- Improved Data Accuracy:HRIS systems provide a single source of truth for employee data, reducing inconsistencies and errors. This ensures accurate reporting and decision-making.
- Enhanced Compliance:HRIS systems help organizations comply with labor laws and regulations by providing tools for managing employee records, tracking compliance requirements, and generating reports.
- Better Employee Engagement:HRIS systems can improve employee engagement by providing self-service portals for accessing information, managing benefits, and submitting requests. They also facilitate communication and feedback.
- Cost Savings:HRIS systems can reduce costs associated with manual processes, such as payroll processing, benefits administration, and employee onboarding.
Examples of How an HRIS Can Streamline HR Processes
Here are some real-world examples of how an HRIS can streamline HR processes for small companies:
- Automated Time Tracking and Attendance:An HRIS can automate time tracking and attendance, eliminating the need for manual time sheets and reducing errors. Employees can use mobile apps or web portals to clock in and out, while managers can monitor attendance and approve time off requests.
- Simplified Onboarding:An HRIS can automate the onboarding process by providing new hires with access to company information, policies, and benefits. It can also facilitate communication with HR and streamline the completion of necessary paperwork.
- Streamlined Performance Reviews:An HRIS can provide a platform for conducting performance reviews, setting goals, and providing feedback. It can automate the review process, track progress, and generate reports for performance analysis.
- Centralized Benefits Administration:An HRIS can manage employee benefits, including health insurance, retirement plans, and time off. It can automate enrollment, track eligibility, and generate reports for compliance purposes.
Choosing the Right HRIS for Small Companies
Choosing the right HRIS system is crucial for small businesses, as it can streamline HR processes, improve efficiency, and enhance employee satisfaction. With numerous HRIS solutions available, selecting the best fit for your unique needs can seem daunting. This section delves into key factors to consider, explores different HRIS solutions, and provides tips for evaluating features and pricing.
Factors to Consider When Selecting an HRIS
Choosing the right HRIS involves evaluating several factors. These factors can help narrow down your options and ensure you select a system that aligns with your company’s needs and goals.
- Company Size and Growth Potential:Consider the current size of your company and your projected growth in the coming years. Select a system that can accommodate your current needs and scale as your business expands.
- Budget:Determine your budget for an HRIS system. Prices vary depending on features, integrations, and the number of employees. Evaluate different pricing models, such as monthly subscriptions or one-time fees.
- Features and Functionality:Identify the core HR processes you want to automate. Prioritize features that align with your current and future needs, such as payroll, benefits administration, time and attendance tracking, performance management, and employee onboarding.
- Integration with Existing Systems:Assess your current technology infrastructure and determine if the HRIS system can integrate with existing applications, such as accounting software, CRM, or payroll systems. Seamless integration can prevent data silos and improve efficiency.
- User-Friendliness and Mobile Accessibility:Choose a system with an intuitive interface that is easy for both HR professionals and employees to navigate. Mobile accessibility is also crucial for employees to access information and complete tasks from anywhere.
- Security and Data Privacy:Ensure the HRIS system prioritizes data security and privacy. Look for features like encryption, multi-factor authentication, and compliance with relevant data privacy regulations.
- Customer Support and Training:Evaluate the level of customer support and training offered by the vendor. Reliable support can be crucial for troubleshooting issues and ensuring the system is used effectively.
Different HRIS Solutions for Small Businesses
The HRIS market offers various solutions tailored to meet the needs of small businesses. Here’s a comparison of different HRIS solutions:
- Cloud-Based HRIS:These solutions are hosted on a third-party server and accessible via the internet. They offer flexibility, scalability, and affordability, making them popular among small businesses. Examples include BambooHR, Gusto, and Paychex Flex.
- On-Premise HRIS:These solutions are installed and managed on a company’s servers. They offer greater control over data and security but require significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance.
- Open-Source HRIS:These solutions are free to use and modify. While they offer cost savings, they may require technical expertise for implementation and maintenance. Examples include OrangeHRM and Odoo.
Evaluating HRIS Features and Pricing
When evaluating HRIS features and pricing, consider the following tips:
- Identify Essential Features:Create a list of essential features based on your company’s needs. Prioritize features that will have the most significant impact on your HR processes.
- Compare Feature Sets:Compare the feature sets of different HRIS systems. Look for systems that offer the essential features you need and additional features that might be valuable in the future.
- Consider Pricing Models:Evaluate different pricing models, such as monthly subscriptions, per-employee fees, or one-time purchase options. Choose a pricing model that aligns with your budget and provides the best value for your investment.
- Request Demonstrations:Request demonstrations from shortlisted vendors to see the HRIS system in action. This will give you a better understanding of the user interface, features, and functionality.
- Read Reviews and Testimonials:Read reviews and testimonials from other small businesses that have used the HRIS systems you are considering. This can provide valuable insights into the system’s strengths, weaknesses, and customer support.
Implementing an HRIS System

Implementing an HRIS system is a significant step for any small company. It requires careful planning and execution to ensure a smooth transition and maximize the benefits of the new system.
Steps Involved in Implementing an HRIS System
The implementation process involves several key steps, each crucial for successful adoption.
- Define Project Scope and Objectives:Clearly define the goals of the HRIS implementation. Identify specific HR processes that will be automated, the desired outcomes, and the key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure success.
- Select and Configure the System:Choose an HRIS system that aligns with the company’s needs and budget. Consider factors like ease of use, features, integration capabilities, and vendor support. Once selected, configure the system to match the company’s specific HR processes and data structures.
- Data Migration and Integration:Transfer existing HR data from legacy systems or spreadsheets into the new HRIS. This step requires careful planning and validation to ensure data accuracy and completeness. Integrate the HRIS with other systems, such as payroll, time and attendance, and benefits administration, to streamline processes.
- User Training and Adoption:Train employees on how to use the new HRIS system effectively. Provide comprehensive training materials, including online tutorials, user guides, and interactive demos. Encourage early adoption and provide ongoing support to address user queries and concerns.
- Testing and Go-Live:Thoroughly test the HRIS system before launching it to ensure functionality and data integrity. Conduct pilot testing with a small group of users to identify and resolve any issues. Once satisfied with the system’s performance, schedule a go-live date and communicate it clearly to all stakeholders.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Optimization:Continuously monitor the HRIS system’s performance and identify areas for improvement. Gather user feedback, track KPIs, and make necessary adjustments to optimize system utilization and effectiveness.
Strategies for Employee Training
Effective training is crucial for successful HRIS adoption.
- Personalized Training Programs:Design training programs that cater to the specific needs and skill levels of different employee groups. Offer tailored training materials and sessions to address the unique requirements of each role.
- Interactive Learning Methods:Incorporate interactive elements into training, such as simulations, role-playing exercises, and online quizzes. This approach enhances engagement and retention of information.
- On-Demand Training Resources:Provide employees with access to online training materials, tutorials, and FAQs. This allows them to learn at their own pace and revisit information as needed.
- Mentorship and Support:Assign experienced employees as mentors to new users. Provide ongoing support through dedicated help desks, online forums, or email communication channels.
Managing Data Migration and Integration
Data migration and integration are critical steps in HRIS implementation.
- Data Mapping and Validation:Carefully map data fields from legacy systems to the new HRIS. Validate data accuracy and completeness through thorough checks and comparisons.
- Data Cleansing and Transformation:Cleanse data by removing duplicates, inconsistencies, and errors. Transform data into the required format and structure for the new HRIS.
- Data Backup and Recovery:Create backups of all data before migration. Establish disaster recovery plans to ensure data integrity and availability in case of unforeseen events.
- Integration Testing:Test the integration between the HRIS and other systems, such as payroll, time and attendance, and benefits administration. Ensure data flows seamlessly and accurately between systems.
HRIS Features for Small Companies

HRIS systems are designed to simplify and streamline various HR functions for businesses of all sizes, including small companies. By automating tasks and providing a centralized platform for managing employee data, HRIS systems can significantly improve efficiency, accuracy, and compliance in HR operations.
This section will delve into the specific features that HRIS systems offer to small businesses, highlighting their benefits and practical applications.
Managing Employee Data
HRIS systems act as a centralized repository for storing and managing employee data, including payroll, benefits, and time off. This data is readily accessible to authorized personnel, eliminating the need for manual record-keeping and reducing the risk of errors.
Payroll Management
HRIS systems can automate payroll processing, ensuring accurate and timely payments to employees. They can integrate with payroll software, enabling seamless data transfer and reducing the risk of manual errors.
- Time Tracking:HRIS systems can track employee hours worked, including overtime, breaks, and sick leave. This information is automatically integrated into payroll calculations, ensuring accurate payment for all hours worked.
- Deductions and Taxes:HRIS systems can automatically deduct taxes, insurance premiums, and other required deductions from employee paychecks. They also handle tax reporting and compliance, simplifying payroll management for small businesses.
- Direct Deposit:HRIS systems can facilitate direct deposit of employee paychecks, reducing the need for physical checks and improving the efficiency of payroll processing.
Benefits Administration
HRIS systems can manage employee benefits, including health insurance, retirement plans, and other perks. They provide a platform for employees to enroll in benefits, track their coverage, and make changes to their plans as needed.
- Benefit Enrollment:HRIS systems simplify the process of enrolling in benefits, allowing employees to select their desired plans and make changes online. This reduces administrative burden for HR staff and ensures accurate enrollment data.
- Open Enrollment:HRIS systems can manage open enrollment periods, allowing employees to review and update their benefit selections. They also provide automated reminders and notifications, ensuring that employees are aware of deadlines and important information.
- Benefit Tracking:HRIS systems track employee benefits, including coverage details, premiums, and claims history. This information is easily accessible to both employees and HR staff, providing transparency and simplifying benefit management.
Time Off Management
HRIS systems streamline time off management by providing a centralized platform for employees to request and track time off. This reduces the risk of conflicting requests and ensures that managers have a clear understanding of employee absences.
- Time Off Requests:HRIS systems allow employees to submit time off requests electronically, simplifying the process and reducing administrative burden. They also ensure that requests are properly documented and approved according to company policies.
- Time Off Tracking:HRIS systems track employee time off, including vacation, sick leave, and other types of absences. This information is readily accessible to managers, allowing them to monitor employee attendance and plan for staffing needs.
- Accrual Tracking:HRIS systems can track the accrual of time off benefits, ensuring that employees are aware of their available time off and preventing unauthorized usage.
Recruiting and Onboarding
HRIS systems can play a significant role in the recruiting and onboarding process for new employees, automating tasks and streamlining the overall experience.
Applicant Tracking
HRIS systems can manage the entire recruiting process, from posting job openings to tracking applications and scheduling interviews. This simplifies the process for HR staff and improves the candidate experience.
Expand your understanding about Exploring HVAC Software for Small Businesses with the sources we offer.
- Job Posting:HRIS systems can be used to post job openings on various platforms, including company websites, job boards, and social media. This increases the reach of job postings and attracts a wider pool of qualified candidates.
- Application Tracking:HRIS systems track applications received, allowing HR staff to easily manage and filter candidates based on specific criteria. They also provide a centralized repository for all application materials, ensuring that important documents are readily available.
- Interview Scheduling:HRIS systems can automate interview scheduling, sending reminders and confirmations to both candidates and interviewers. This reduces administrative burden and improves the efficiency of the interview process.
Onboarding
HRIS systems can automate the onboarding process for new employees, providing a seamless and efficient experience.
- New Hire Forms:HRIS systems can collect new hire information electronically, including personal details, tax information, and emergency contacts. This simplifies the onboarding process and reduces the need for manual paperwork.
- Employee Handbook Access:HRIS systems can provide new hires with access to the employee handbook and other important company documents online. This ensures that employees have access to essential information from the start.
- Benefits Enrollment:HRIS systems can facilitate benefit enrollment for new hires, allowing them to select their desired plans and make changes online. This simplifies the benefits process and ensures that employees are properly enrolled.
Cost Considerations for HRIS Systems
Implementing an HRIS system can be a significant investment for small businesses. While the benefits are undeniable, it’s crucial to understand the associated costs to make informed decisions. This section will delve into various cost factors, explore return on investment (ROI), and discuss strategies for budgeting and managing HRIS expenses.
Cost Comparison of HRIS Solutions
The cost of HRIS solutions varies widely depending on several factors, including the size of your company, the features you require, and the provider you choose. It’s essential to compare different options to find the best fit for your budget and needs.
- Cloud-based HRIS:Cloud-based systems typically offer subscription-based pricing models, with monthly or annual fees. These fees can vary based on the number of employees, features included, and support services offered. For example, a small business with 50 employees might pay between $50 to $100 per employee per month for a basic cloud-based HRIS.
- On-premise HRIS:On-premise systems require upfront investment in hardware, software, and installation. The initial cost can be substantial, but you may have lower ongoing expenses. For example, an on-premise HRIS for a small business with 50 employees could cost around $10,000 to $20,000 upfront.
- Open-source HRIS:Open-source systems are free to use, but you may need to pay for customization, support, and maintenance. These costs can vary depending on the complexity of your needs.
Calculating Return on Investment (ROI)
While the initial cost of implementing an HRIS system can be substantial, the potential benefits can significantly outweigh the investment. The ROI of an HRIS system can be calculated by considering the cost savings and efficiency gains generated by the system.
ROI = (Benefits
Costs) / Costs
For example, a small business that automates its payroll process using an HRIS system might save $5,000 per year in labor costs. If the HRIS system costs $10,000 to implement, the ROI would be:
ROI = ($5,000
- $10,000) / $10,000 =
- 50%
However, this calculation only considers the cost savings from payroll automation. The HRIS system might also generate benefits like reduced employee turnover, improved employee engagement, and better data-driven decision-making. These benefits are difficult to quantify but can significantly contribute to the overall ROI.
Strategies for Budgeting and Managing HRIS Costs
Budgeting and managing HRIS costs effectively is crucial for maximizing the value of your investment. Here are some strategies:
- Negotiate with providers:Many HRIS providers offer discounts for small businesses, especially for long-term contracts. Don’t hesitate to negotiate for a better price.
- Consider a phased implementation:Implementing an HRIS system in phases can help you control costs. Start with essential features and gradually add more functionality as your budget allows.
- Maximize system utilization:Ensure your employees are fully trained and utilize all the features of the HRIS system. This can help you avoid unnecessary costs associated with manual processes.
- Monitor system performance:Regularly monitor the performance of your HRIS system to identify areas for improvement. This can help you optimize costs and avoid unnecessary expenses.
Security and Compliance
An HRIS system stores a wealth of sensitive employee data, including personal information, payroll details, and performance records. Protecting this data is paramount, and a robust security and compliance framework is crucial for any small business using an HRIS.
Data Security Best Practices
Data security is paramount to safeguarding sensitive employee information. Here are key practices to implement:
- Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication:Require employees to use strong passwords with a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for added security, requiring users to provide an additional form of verification, such as a code sent to their mobile device, after entering their password.
- Regular Security Audits:Conduct regular security audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities. This includes testing for security flaws, reviewing access permissions, and ensuring compliance with industry best practices.
- Data Encryption:Encrypt all sensitive data at rest and in transit. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the appropriate decryption key.
- Employee Training:Educate employees about data security best practices, including password hygiene, phishing awareness, and proper data handling procedures.
- Access Control:Implement role-based access control (RBAC) to restrict access to sensitive data based on employee roles and responsibilities. This ensures that only authorized individuals can view and modify specific data.
Compliance with Privacy Regulations
Compliance with privacy regulations is crucial for protecting employee data and avoiding legal repercussions.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR):If your company operates within the European Union or processes data of EU residents, you must comply with GDPR. This regulation mandates data minimization, transparency, and individual rights related to their data.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA):If your company operates in California or processes data of California residents, you must comply with CCPA. This law grants California residents the right to know, access, delete, and opt-out of the sale of their personal data.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA):If your company handles health information, you must comply with HIPAA. This law sets standards for protecting the privacy and security of patient health information.
Protecting Sensitive Employee Information
Here are specific measures to protect sensitive employee information:
- Data Minimization:Only collect and store data that is absolutely necessary for business operations. Avoid collecting unnecessary information that could be misused or compromised.
- Data Retention Policies:Establish clear data retention policies that Artikel how long different types of data will be stored. Regularly review and update these policies to ensure compliance with regulations and best practices.
- Secure Data Storage:Store sensitive employee data in secure, encrypted databases with appropriate access controls. Consider using cloud-based storage solutions with robust security features.
- Regular Backups:Regularly back up all data to prevent loss due to hardware failure or cyberattacks. Ensure that backups are stored securely and are regularly tested for recovery.
Future Trends in HRIS
The HRIS landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing business needs. Emerging trends are shaping the future of HRIS, offering new opportunities for small companies to streamline their HR processes and improve employee engagement.
The Impact of Cloud Computing and Mobile Accessibility, HRIS Systems for Small Companies
Cloud computing and mobile accessibility have significantly impacted HRIS systems, making them more accessible and affordable for small businesses. Cloud-based HRIS solutions are hosted on remote servers, eliminating the need for on-premises infrastructure and IT maintenance. This allows small businesses to access HRIS functionalities from anywhere with an internet connection, enhancing flexibility and collaboration.
- Reduced IT Costs:Cloud-based HRIS eliminates the need for expensive hardware and software licenses, significantly reducing IT infrastructure costs.
- Enhanced Accessibility:Employees can access HRIS systems from any device with an internet connection, promoting remote work and flexible work arrangements.
- Scalability:Cloud-based HRIS solutions can easily scale to meet the evolving needs of a growing business without requiring significant investments in infrastructure.
- Automatic Updates:Cloud providers handle software updates and maintenance, ensuring that HRIS systems are always up-to-date and secure.
The Potential of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in HRIS
AI is revolutionizing various industries, and HR is no exception. AI-powered HRIS systems can automate repetitive tasks, analyze data to identify patterns, and provide insights for better decision-making.
- Automated Task Management:AI can automate tasks such as payroll processing, time and attendance tracking, and performance reviews, freeing up HR professionals to focus on strategic initiatives.
- Data-Driven Insights:AI algorithms can analyze large datasets to identify trends in employee performance, attrition rates, and training needs, providing valuable insights for HR decision-making.
- Personalized Employee Experiences:AI can personalize employee experiences by recommending relevant training programs, suggesting career paths, and providing personalized communication based on individual needs.
- Improved Candidate Screening:AI-powered recruitment tools can automate candidate screening, identifying the most qualified applicants based on specific criteria.
Last Word
Implementing an HRIS system is a strategic decision that can significantly impact a small company’s growth and success. By carefully choosing the right system, integrating it effectively, and leveraging its features, small businesses can gain a competitive advantage by optimizing their HR processes, fostering a positive work environment, and driving business outcomes.
As HRIS technology continues to evolve, small companies can embrace its potential to stay ahead of the curve and thrive in the ever-changing business landscape.
Popular Questions: HRIS Systems For Small Companies
What are the common challenges faced by small companies when implementing an HRIS system?
Small companies often face challenges such as limited resources, budget constraints, and a lack of in-house IT expertise. However, cloud-based HRIS solutions and affordable options are increasingly available, making implementation more accessible.
How can I determine the right HRIS system for my small company?
Consider your company’s specific needs, budget, number of employees, and industry. Research different HRIS providers, compare features, pricing, and customer reviews. It’s also essential to evaluate the system’s ease of use, integration capabilities, and support services.
What are the benefits of using an HRIS system for employee engagement?
HRIS systems can enhance employee engagement by providing self-service portals for accessing information, managing benefits, and requesting time off. They can also facilitate communication, streamline performance reviews, and provide opportunities for professional development.